What is Kelly Criterion?
The Kelly criterion optimises asset growth by allocating a fixed fraction of wealth across multiple investments. The concept is often employed in the gambling industry.

A Short Example
You own a biased coin with a probability of landing heads up ![]()
$1,000. How much of this should you wager?
A Deep Dive into Kelly Criterion
Let’s continue with the preceding example. The first tip is to wager in accordance to your available funds. As your fortune grows, you can increase your betting amount. However, avoid placing too much amount. If you wager the entire $1000, you will eventually lose and be unable to continue. If you risk too little, it will take a long time to earn a reasonable amount.
The Kelly criterion is to bet a certain fraction of your wealth so as to maximize your expected growth of wealth.
We use ![]()
1 with probability p and −1 with probability 1 - p, and f to represent the fraction of our income that we gamble. Tossing the coin generates a random quantity of wealth.
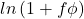
The expected growth rate is
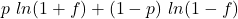
This function is plotted below for p = 0.55.
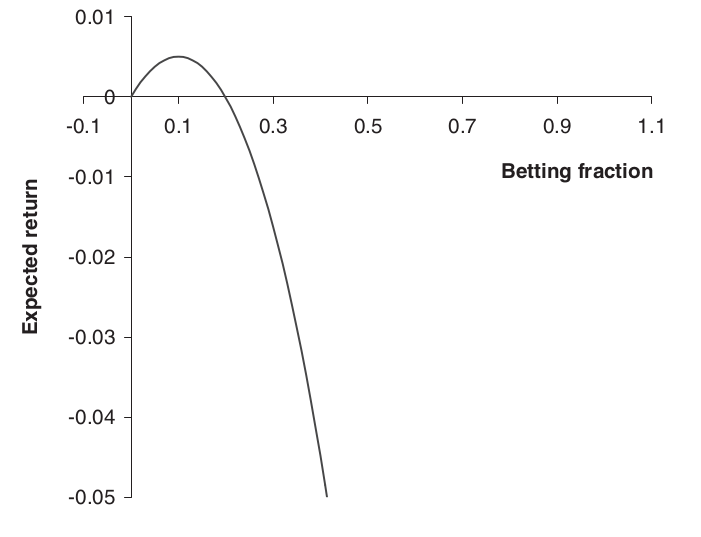
This expected growth rate is maximized by the choice f = 2p − 1. This is the Kelly fraction
The Sweet Spot: Finding Optimal Bet Size
A betting fraction below this would be a conservative strategy. Moving to the right increases volatility and decreases projected returns. Moving too far to the right can result in a negative expected return.
This money management theory applies to all bets and investments, not just coin tosses.
In general, if an investment has an expected return of ![]()
![]()
f is
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com E[ln(1 + f\phi)]](https://thewhisperingvoid.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-24bb94d7bb44fce10f0955df0e141776_l3.png)
which can be approximated by Taylor series
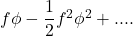
The Kelly fraction, obtained by maximising this expression, is
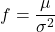
When estimating the mean and standard deviation, it’s best to be conservative and stake a smaller proportion. A popular choice is half Kelly.
Other money management tactics, such as targeting wealth or predicting ruin, are also available.
Related Readings
- Modern Portfolio Theory in Finance
- Arbitrage in Quantitative Finance: All You Need To Know
- Modelling Approaches in Quantitative Finance: All You Need To Know
- Put-Call Parity: All You Need To Know